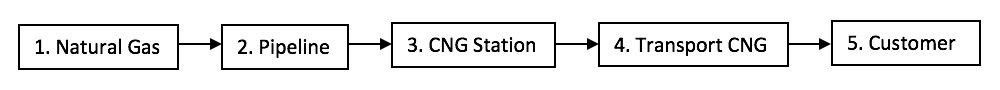With the volatile world’s oil price and that Indonesia’s continuous rise of demand for energy, natural gas has become one of the most searchable and favored alternative source of energy. Natural Gas are considered because not only is a clean energy fuel (“environmental green energy”) consisting primary of methane (CH4), but also is an ideal substitute for other energy fuel like gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, and even liquid petroleum gas (LPG) because of its higher octane and relatively stable pricing among those choice of energies.
Indonesia is already known for its abundant supply of natural gas, in which based on 2012 BP World Energy Report has the largest proven gas reserves in Asia Pacific. With a proven reserve of 112,5 TSCF and level of production reaching 3,02 TSCF per year, the reserve to production ratio (R/P) of Indonesia natural gas is expected to reach more than 30 years. This natural gas can be found in many gas fields across Indonesia.
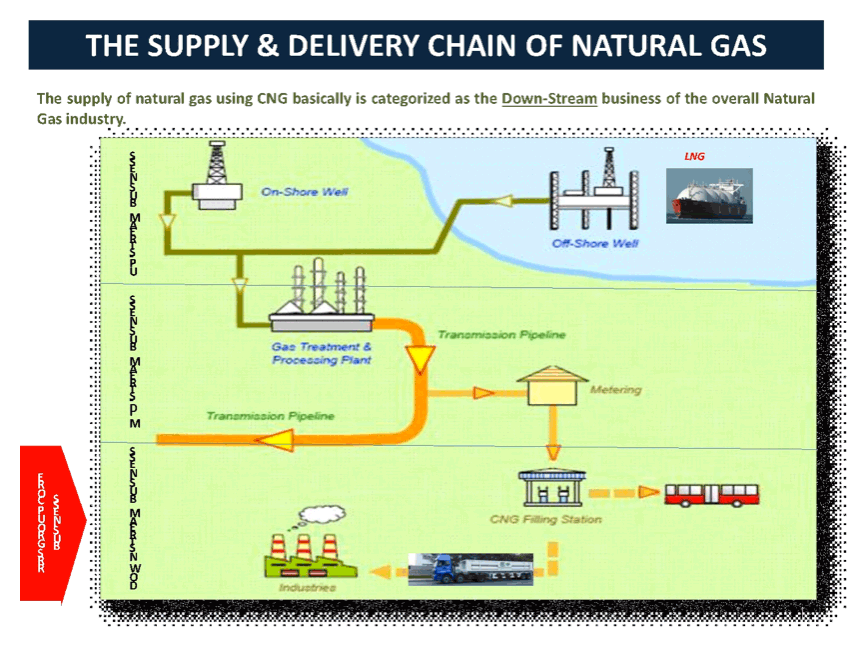
Natural gas can be delivered to the end users through 3 (three) medium forms of distribution, which are through pipeline gas (NG), liquefied natural gas (LNG), and compressed natural gas (CNG). The most common on shore distribution of natural gas had been done through the medium of pipeline distribution.
However, up until today, these pipeline distributions of natural gas in Indonesia are still not widely available to all end users that are spread un-evenly around the Indonesian archipelago. Due to the location of the source of biomethane are far away and unfeasible to extend such media of gas delivery through pipeline, there is an alternative way of the delivery of the biomethane that is through CNG, which uses the concept of a virtual pipeline.
The premise of the virtual pipeline is that biomethane gas and natural gas can be economically handled and transported effectively to any locations where a logistic vehicle can go. Using CNG technology, the natural gas is compressed at a very high pressure up to 250 kg/cm2 (bar) and stored in a several CNG cylinder, which are put together as a cascade and each tank is connected with one another.
The cascade cylinders then are delivered using truck fleet to the customers designated area. The volume of gas that can be delivered per trip is depended upon the type of transportation mode being used. The bigger the capacities of the truck fleet, the more cascade able to be transported, hence, the larger amount of volume of gas that is being distributed.
In addition, aside of the size of the cylinder containers skid carrying the compressed natural gas, other factors that will determine the price of CNG are as follow:
- Well Head & Piping Toll Fee Gas Price.
- CNG Station Compression Cost.
- Delivery Distance from CNG Station to Customer Site.
- Size of Contract or Volume of CNG needed per day.
- Contract Period.
- Terms of Payment.
All those factors above will determine the investment and cost evaluation in which will result to the end price of CNG as depicted in table below:
Given the brief information above of how natural gas can be used as a substitution fuel for diesel petrol, LPG, and coal, we as RRS Group can provide full-service of the entire CNG value chain from gas retrieval, gas compression, CNG transport, and CNG delivery at the customer end.